Genetic therapy corrects progressive muscle disorder in mice
People with myotonic dystrophy experience progressive muscle weakness and repeated episodes of painless muscle stiffness called myotonia.
Investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) recently used a targeted drug to restore muscle strength and correct myotonia in mice with myotonic dystrophy. The research, which is published in Nature Communications, could lead to new treatments for affected patients.
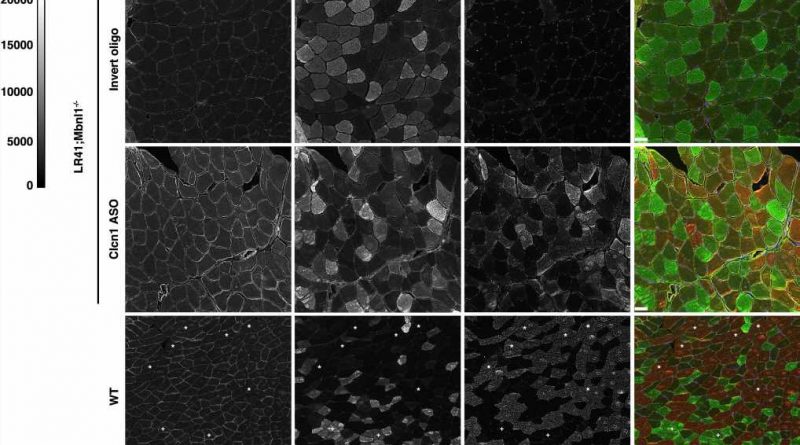
Myotonia in myotonic dystrophy is caused by abnormal processing (or splicing) of the transcript created from the gene that codes for the muscle chloride channel Clcn1, a protein that controls the flow of chloride ions into muscle cells.
The abnormal splicing leads to a truncated and poorly functioning Clcn1.
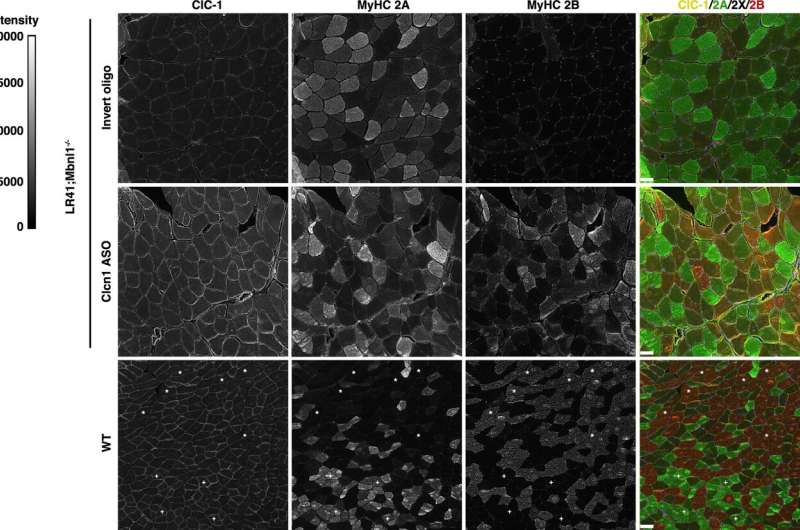
Also, the degree of weakness in patients with myotonic dystrophy is associated with higher amounts of oxidative—rather than glycolytic—muscle fibers. These fibers differ in how they obtain energy for contraction.
To correct the abnormal splicing in mice with myotonic dystrophy, a team led by Thurman Wheeler, MD, a neuromuscular researcher at MGH and an associate professor of Neurology at Harvard Medical School, used a genetic therapy involving small pieces of DNA called antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs).
The ASOs were based on a code that targets the abnormal splicing of Clcn1, and when injected directly into the animals’ muscles, the ASOs corrected the abnormality, boosted the abundance of functional Clcn1, increased the amount of glycolytic muscle fibers, and restored muscle health.
“Our findings show that muscle fiber type transitions in myotonic dystrophy result from myotonia and are reversible,” says Wheeler. “Our results also support Clcn1-targeting therapies as a way to increase strength and reduce muscle injury in patients.”
Additional co-authors include Ningyan Hu, Eunjoo Kim, and Layal Antoury.
More information:
Ningyan Hu et al, Correction of Clcn1 alternative splicing reverses muscle fiber type transition in mice with myotonic dystrophy, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-37619-1
Journal information:
Nature Communications
Source: Read Full Article