National Qatari study shows vaccination reduces risk of spreading SARS-CoV-2 infection
A team of scientists from Qatar and the United States has recently studied the viral transmission potential of individuals with primary severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, reinfection, or vaccine breakthrough infection. The findings reveal that unvaccinated individuals with primary infection are 50% more likely to transmit infection than vaccinated individuals with breakthrough infections. The study is currently available on the medRxiv* preprint server.
.jpg)
Background
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines currently rolling out globally have shown strong protective efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 infection and symptomatic COVID-19. However, there is accumulating evidence suggesting that the vaccines may not always induce sterilizing immunity against infections caused by novel viral variants. Although multiple vaccine breakthrough infections have been identified in many countries, it is still uncertain whether these cases are infectious enough to transmit the virus to others. In this context, it is generally assumed that vaccine-induced reduction in viral replication and subsequent viral load account for faster clearance of infection and lesser possibility of viral transmission.
In the current study, scientists have investigated the effect of vaccination on viral transmission potential by comparing viral loads in vaccinated individuals with breakthrough infections and unvaccinated individuals with primary infection. Moreover, they have investigated the effect of previous infection on reinfection in unvaccinated individuals. For this purpose, they have compared the viral loads in individuals with SARS-CoV-2 reinfection or primary infection.
Study design
As a measure of viral load, the scientists analyzed polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-generated cycle threshold (Ct) values of 384,452 individuals with primary infections, 1,695 with reinfection, 4,777 with BNT162b2 (Pfizer/BioNTech) breakthrough infections, and 306 with mRNA-1273 (Moderna) breakthrough infections.
The BNT162b2 breakthrough infections occurred in 0.61% of fully vaccinated population, and the mRNA-1273 breakthrough infections occurred in 0.09% of fully vaccinated population.
Important observations
Among all PCR-confirmed infections, breakthrough infections in vaccinated or previously infected individuals exhibited lower viral loads than primary infections in unvaccinated individuals. Specifically, the viral load was lowest in unvaccinated individuals with reinfection, followed by mRNA-1273 breakthrough infections and BNT162b2 breakthrough infections sequentially.
Similar findings were obtained in analyzes that included only randomly diagnosed asymptomatic infections. However, by limiting the analysis to only symptomatic infections, the lowest viral load was observed in mRNA-1273 breakthrough infections, followed by reinfections and BNT162b2 breakthrough infections sequentially. Notably, among all mRNA-1273 breakthrough infections, very few were symptomatic.
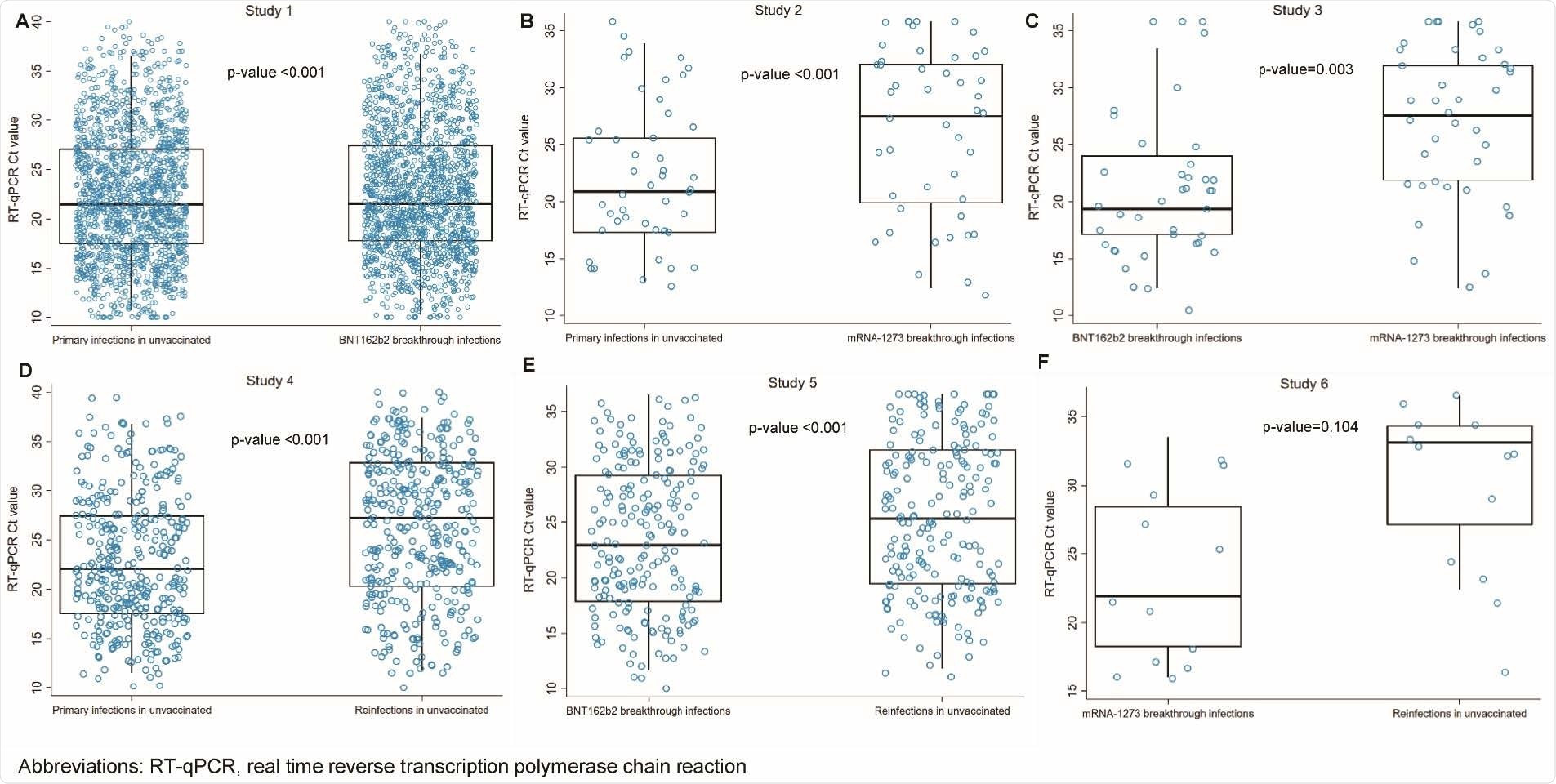
Infectiousness of breakthrough infections
It is empirically assumed that viral load is directly proportional to the volume of infectious viruses. Estimations made in the study from this assumption revealed that breakthrough infections in vaccinated or previously infected individuals had significantly lower infectiousness compared to primary infections in unvaccinated individuals.
The analyses, including randomly diagnosed asymptomatic and symptomatic infections, revealed that the level of infectiousness was highest in primary infections, followed by BNT162b2 breakthrough infections, mRNA-1273 breakthrough infections, and reinfections sequentially.
Specifically, BNT162b2 breakthrough infections, mRNA-1273 breakthrough infections, and reinfections were only 0.41-fold, 0.11-fold, and 0.06-fold as infectious as primary infections, respectively.
Study significance
The study demonstrates that individuals having immunity against SARS-CoV-2 from vaccination or prior infection are more likely to have lower viral loads upon infection/reinfection. In addition, since viral load is directly correlated with the amount of culturable or infectious viruses, the study findings indicate that the risk of viral transmission from vaccinated or previously infected individuals is relatively lower than that from unvaccinated individuals with primary infection.
Overall, the study highlights that COVID-19 vaccines are effective in reducing the rate of person-to-person viral transmission, in addition to preventing primary SARS-CoV-2 infections.
*Important Notice
medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information
- Abu-Raddad LJ. 2021. Effect of vaccination and of prior infection on infectiousness of vaccine breakthrough infections and reinfections, medRxiv, https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.28.21261086, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.07.28.21261086v1
Posted in: Medical Research News | Disease/Infection News
Tags: Coronavirus, Coronavirus Disease COVID-19, CT, Efficacy, Healthcare, immunity, Polymerase, Polymerase Chain Reaction, Respiratory, SARS, SARS-CoV-2, Severe Acute Respiratory, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, Syndrome, Vaccine, Virus

Written by
Dr. Sanchari Sinha Dutta
Dr. Sanchari Sinha Dutta is a science communicator who believes in spreading the power of science in every corner of the world. She has a Bachelor of Science (B.Sc.) degree and a Master's of Science (M.Sc.) in biology and human physiology. Following her Master's degree, Sanchari went on to study a Ph.D. in human physiology. She has authored more than 10 original research articles, all of which have been published in world renowned international journals.
Source: Read Full Article
