Two-stage transplantation is a viable treatment option for liver metastases, shows study
In non-cirrhotic liver diseases, organ transplantation in two steps, especially with a living donation, is a safe therapy option for donors and recipients. This is the conclusion of a case series evaluated by surgeons from the Jena University Hospital in Annals of Surgery. When patients have normal organ function e.g. in the case of liver metastases, no donor organs are available according to waiting list criteria.
More than 1,200 patients were listed waiting for a liver transplant in Germany in 2021. The most frequent reason for this was liver cirrhosis, in which the tissue of the central metabolic organ loses its function due to chronic inflammation, alcohol damage or poisoning.
But cancer can be the reason to need a new liver, too. This includes unresectable metastases in the liver descending from tumors in other organs. However, these patients hardly have a chance for an organ from a deceased donor because their liver function is less restricted than in the case of cirrhosis and the remaining organ function is a central criterion for the allocation of the rare donor organs.
In addition to the transplantation of the organs of the deceased, the transplantation surgery team of Jena University Hospital pursues a successful living liver donation program. After an ethics committee verification, healthy people may donate a partial organ to replace the diseased liver. Both the transplanted part and the remaining organ assume full organ function, because of the particular regeneration ability of the liver.
Living donation in the two-step procedure
“It is the continuing shortage of donor organs that motivates and drives our clinical and scientific work in this area,” Prof. Dr. Utz Settmacher, Director of the Department of General, Visceral and Vascular Surgery, says.
In cooperation with colleagues from Brussels, Padua, Oslo, Munich and Tübingen, the Jena surgeons published in Annals of Surgery their transplantation experiences in patients who mostly suffer from colon cancer metastases in the liver.
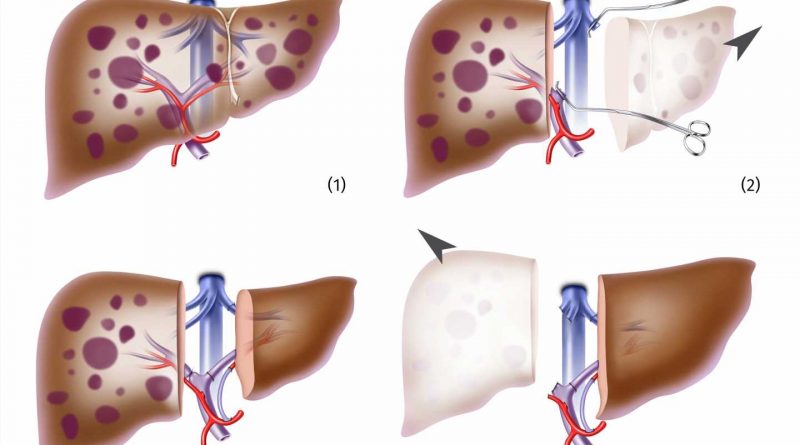
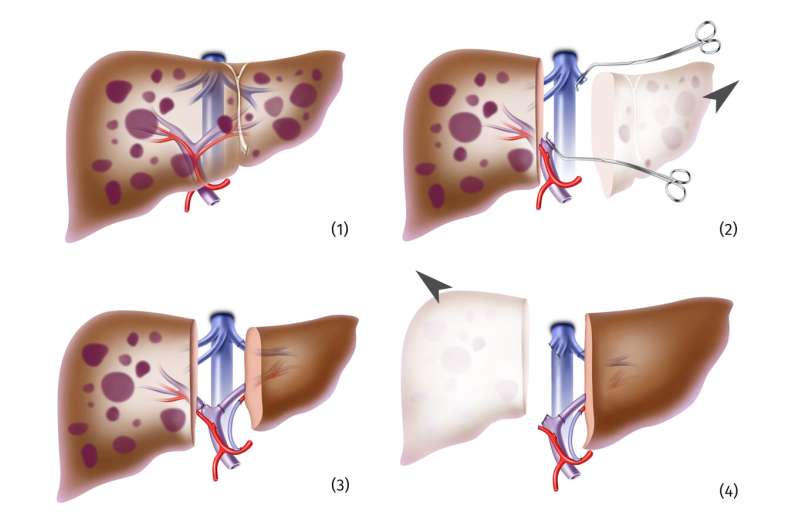
The transplantations were performed in a two-step procedure. To protect the donor, the smallest possible liver section was removed and transplanted. The recipient initially retained a part of the diseased liver to ensure organ function. However, the surgeons reduced the blood flow to this part of the liver to encourage growth of the graft. After about two weeks, it adopts complete organ function and the remaining diseased liver is removed.
Twenty of the 23 patients analyzed in the study were treated with living liver donation. Three received a part of the organ from a deceased donor, and the other organ parts were also transplanted. Most study patients suffered from inoperable metastases from colorectal cancer. Senior author Prof. Dr. Falk Rauchfuss says, “We have compiled and analyzed extensive data on the underlying diseases as well as relevant anatomical and surgical details in order to assess the results in recipients and donors.”
Donor risk minimized and waiting list relieved
Both the organ recipients and the living donors survived the procedures well. Complications that occurred after the operation were comparable to those in similar major procedures and could early be recognized and treated. “The two-stage liver transplant is a treatment option for patients with non-cirrhotic liver diseases that minimizes the donor risk and does not affect the waiting list,” Falk Rauchfuss says.
“Under standardized study conditions, we want to investigate which patient criteria influence the outcome—e.g. short-term and long-term survival or recurrence freedom—in order to gain insights into the dynamics after transplantation. We want to get to know for which patients this therapy fits best,” Utz Settmacher says.
More information:
Utz Settmacher et al, Auxilliary Liver Transplantation According to the RAPID Procedure in Noncirrhotic Patients, Annals of Surgery (2022). DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000005726
Journal information:
Annals of Surgery
Source: Read Full Article