Exosomal lncRNA PCAT-1 promotes Kras-associated chemoresistance
Oncotarget Volume 11, Issue 29 reported that Immunosuppressive chemoresistance is a major burden in lung cancer.
Recent data reveal that long noncoding RNAs present in the lung tumor microenvironment are implicated in chemoresistant-related immune deregulation, and metastasis but their exact pathogenic role is still unknown.
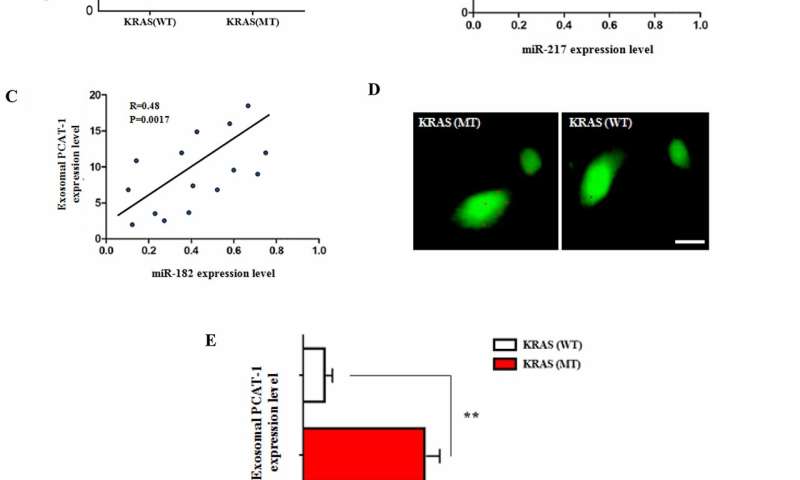
In this study, the Oncotarget authors investigate the role of lncRNA PCAT-1 in chemoresistant immunosuppression and its involvement in tumor stroma remodeling. Findings reveal PCAT-1 to regulate Kras-related lung chemoresistance through increased expression of the immunosuppressive micrornas miR-182/miR217 in lung tissues, thus promoting a pre-metastatic niche formation and a subsequent increase in lung metastatic burden.
Subsequent PCAT-1 knockdown impaired CAF-mediated stromal activation, and reversed chemoresistance and tumor growth in vivo.
Overall, these findings demonstrate the versatile roles of PCAT-1 in sustaining lung immunosuppressive neoplasia through tumor microenvironment remodeling and provide new opportunities for effective metastasis inhibition, especially in chemoresistant tumors.
“Overall, these findings demonstrate the versatile roles of PCAT-1 in sustaining lung immunosuppressive neoplasia through tumor microenvironment remodeling and provide new opportunities for effective metastasis inhibition, especially in chemoresistant tumors”
Dr. Savvas Petanidis from The Aristotle University of Thessaloniki as well as the I.M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University said, “Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related deaths and despite extensive research efforts, the survival rate of lung cancer patients remains significantly low.”
Emerging evidence indicates that lncRNAs present in the lung tumor microenvironment promote tumor growth through cancer cell remodeling that favors immunosuppressive metastasis.
These decisive tumor propagating effects of lncRNA permit tumor cells to bypass immune surveillance and reduce T-cell infiltration into tumor, limiting the clinical benefits of immune checkpoint therapies.
Fibroblasts which play a key role in this mechanism, constitute most of the stromal cells in tumor tissues, secrete a wide spectrum of chemokines or cytokines to the tumor microenvironment, thus promoting growth, invasion, angiogenesis.
Furthermore, fibroblast-derived exosomes induce cancer stem cell expression that contributes to altered tumor metabolism and emergence of chemoresistance in tumor microenvironment.
In this study the authors characterize for the first time the role of lncRNA PCAT-1 in Kras-related lung chemoresistance and its role in tumor stroma remodeling via immunosuppressive miR-182/miR217 expression and fibroblast differentiation.
“In this study the authors characterize for the first time the role of lncRNA PCAT-1 in Kras-related lung chemoresistance and its role in tumor stroma remodeling via immunosuppressive miR-182/miR217 expression and fibroblast differentiation”
Source: Read Full Article
